Why the BMI Calculator for Women Is More Than Just a Number
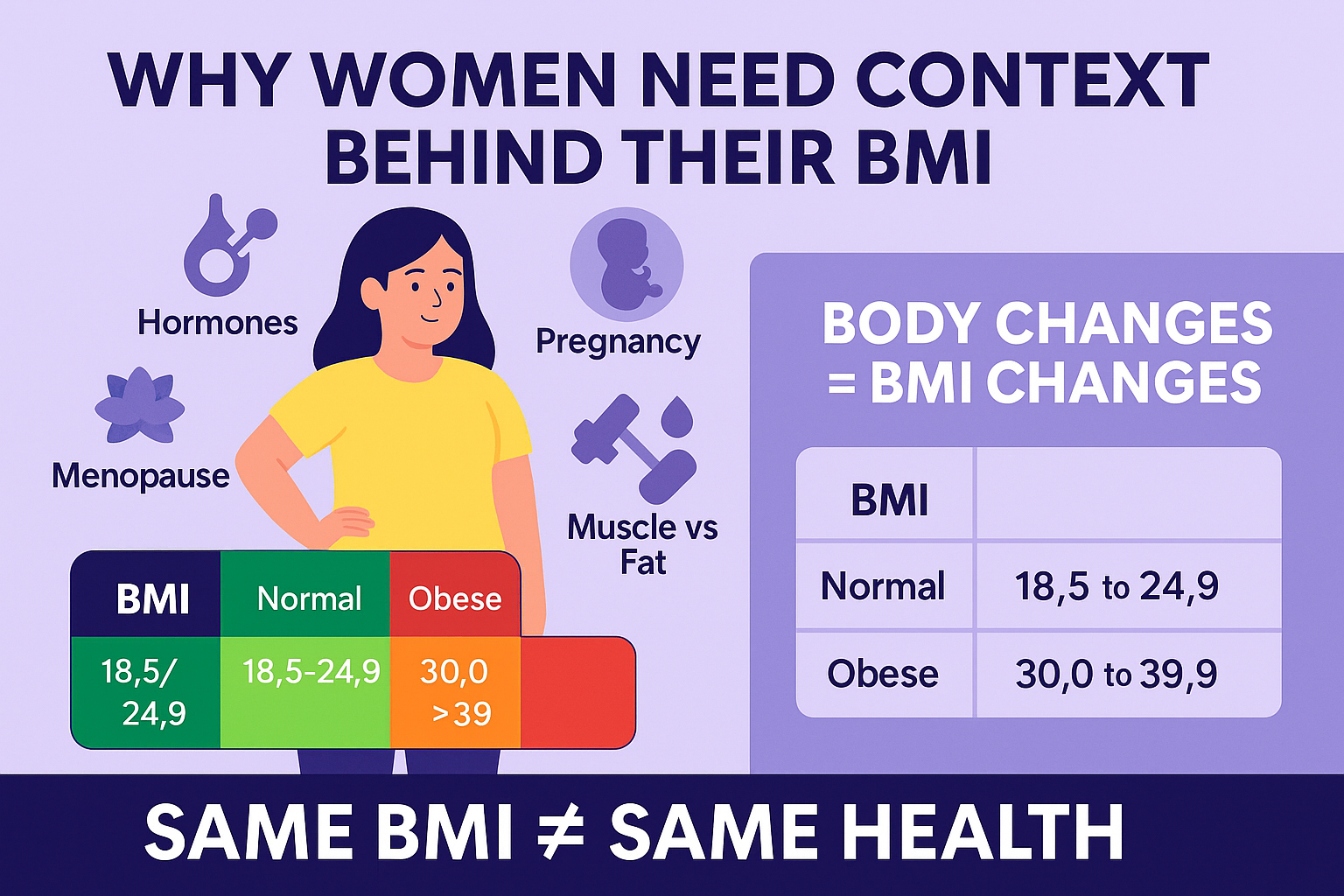
When it comes to measuring health, the BMI Calculator for Women can be a helpful starting point but it doesn’t tell the whole story. While Body Mass Index (BMI) gives a basic measure of weight relative to height, it often misses the physiological realities unique to women’s bodies. This BMI Guide for Women helps you understand how female physiology hormones, pregnancy, menopause, and muscle mass affect your BMI reading.
Women experience distinct hormonal changes throughout life like BMI and pregnancy, menstruation and menopause that influence weight distribution, water retention, and muscle-to-fat ratio. That means two women with the same BMI might be in very different health situations.
That’s why using a BMI calculator for women requires not just inputting numbers but understanding context. In this guide, we’ll explore how to interpret BMI through the lens of female physiology, how to identify a healthy BMI for women, and what to consider during various life stages.
Related Tool: Use the BMI Calculator for Women to get your result, then follow this guide to interpret it accurately.
Or start with the General BMI Calculator if you’re comparing across categories.
Quick Highlights:
- BMI is useful—but incomplete on its own
- Female body composition and hormones impact results
- Learn to read correctly about BMI and pregnancy menstruation, and menopause
- Understand how to use the calculator for long-term health, not just weight tracking
“Don’t just rely on the number your female BMI range must be viewed in the context of age, hormones, and lifestyle.”
How BMI Works: A Practical BMI Guide for Women
What BMI Really Measures And What It Doesn’t
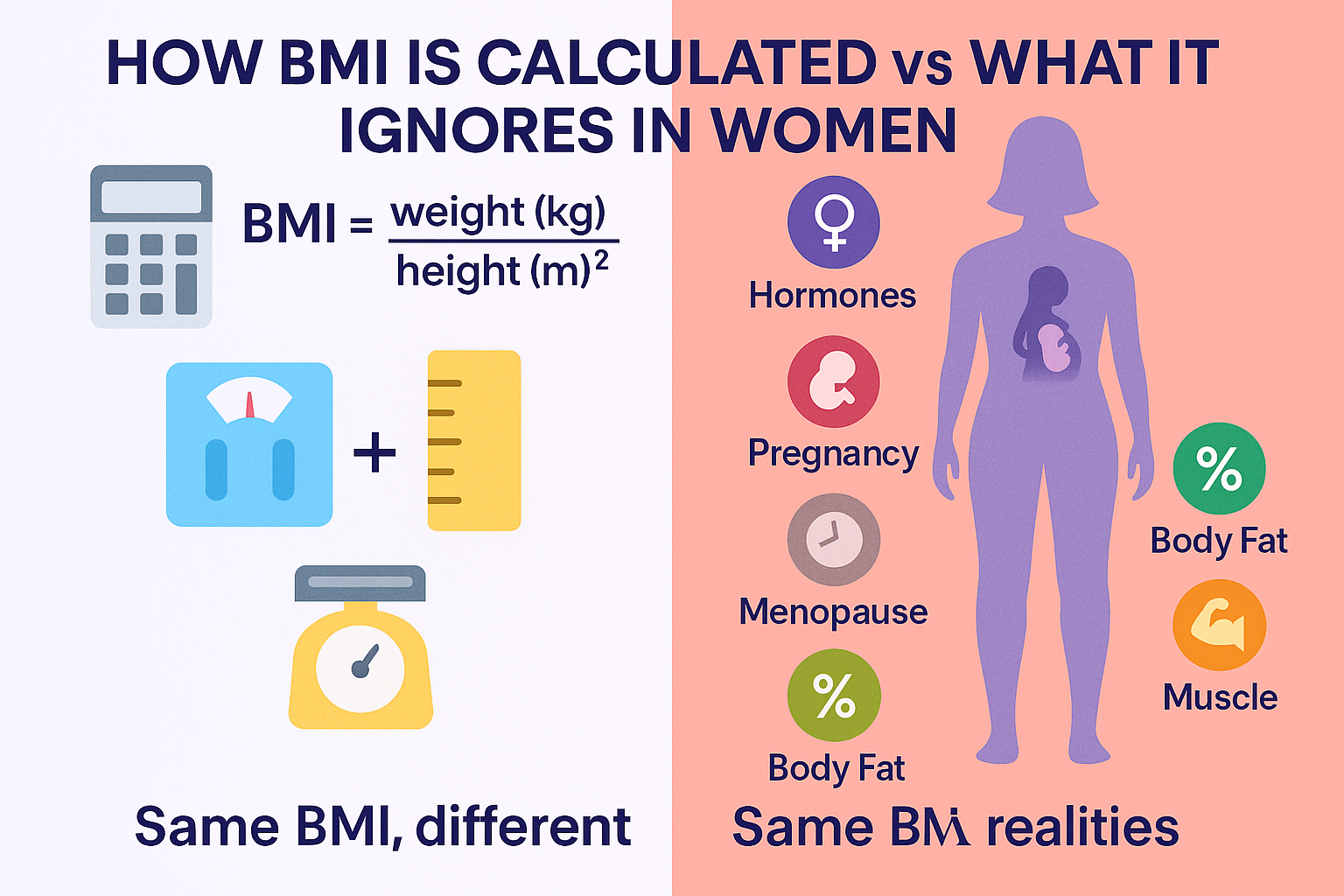
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple calculation: your weight in relation to your height. It helps categorize individuals into ranges like underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
The Standard BMI Formula:
- Metric: BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height (m²)
- Imperial: BMI = (weight (lb) ÷ height (in²)) × 703
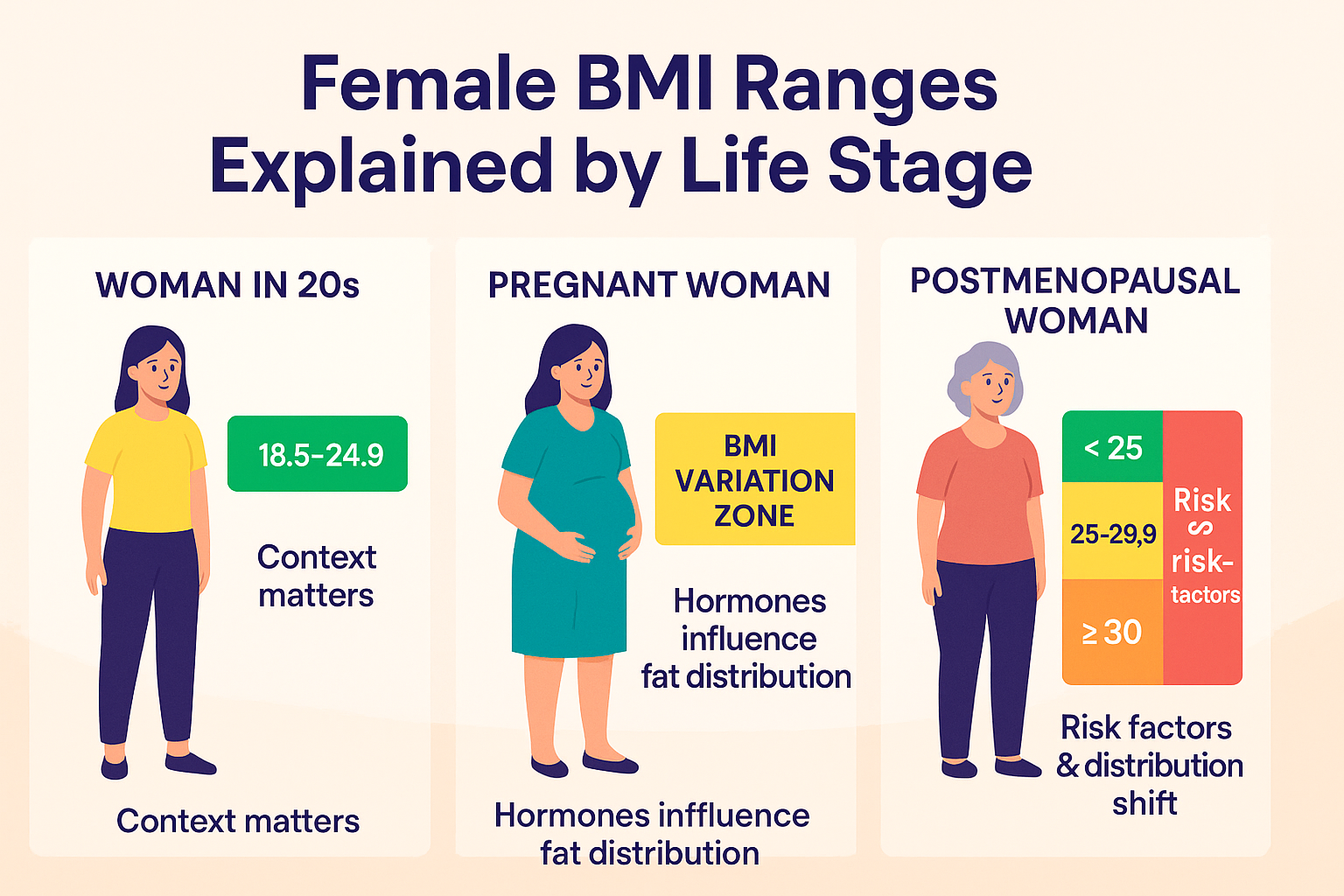
A healthy BMI for women typically falls between 18.5 and 24.9, but this number should always be paired with lifestyle and hormonal context.. For women, understanding your female BMI range helps evaluate where you fall on the scale and whether further assessment is needed.
These formulas are used worldwide by tools like our BMI Calculator for Women and the General BMI Calculator.
But Here’s the Catch for Women:
BMI doesn’t account for:
- Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., water retention during menstruation)
- BMI and Pregnancy weight gain or postnatal changes
- Menopause-related fat redistribution
- Muscle vs fat composition (women often have more body fat naturally)
That’s why many health experts stress that BMI should be viewed as a screening tool, not a complete diagnostic method—especially for women.
Learn more in our BMI Accuracy, Risks & Misconceptions Guide.
Dive into the Science Behind BMI Calculations to understand its limitations in depth.
Learn more about BMI methodology from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“For women, BMI is a rough estimate—not a verdict. Hormones, life stages, and body composition make a big difference in how that number should be read.”
Understanding the Healthy BMI for Women
What’s Considered “Normal” Might Not Be the Same for Everyone
A healthy BMI for women typically falls between 18.5 and 24.9, based on the same standards used for men. But women’s bodies are biologically wired to carry more body fat, especially around the hips, thighs, and breasts due to reproductive hormones like estrogen.
Because of this, BMI categories may require more context when applied to female health especially in active women, pregnant women, or women over 50.
Standard Female BMI Ranges
| BMI Category | BMI Value | What It Means for Women |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Below 18.5 | Possible nutritional deficiencies or hormonal disruption |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 – 24.9 | Generally healthy for most women |
| Overweight | 25 – 29.9 | May carry risks, but depends on muscle/fat ratio |
| Obese (Class I) | 30 – 34.9 | Higher risk of metabolic issues and hormonal imbalances |
| Obese (Class II) | 35 – 39.9 | Requires medical evaluation |
| Obese (Class III) | 40 and above | Very high health risks — professional care advised |
This is why knowing your female BMI range is only the first step—context like fat percentage matters just as much.
Cross-check with our full BMI Calculator Complete Guide to see where you fall and how to act on it.
Important Context:
- Pregnant or postpartum? A temporary increase in BMI is expected.
- Very active? Your BMI may classify you as “overweight” due to muscle, not fat.
- Menopausal? Hormonal shifts can raise BMI without major lifestyle changes.
That’s why BMI should be read alongside other indicators like body fat %, waist circumference, and menstrual regularity.
“A BMI of 24 might mean one thing for a sedentary woman and something totally different for an athlete. Healthy isn’t one-size-fits-all.”
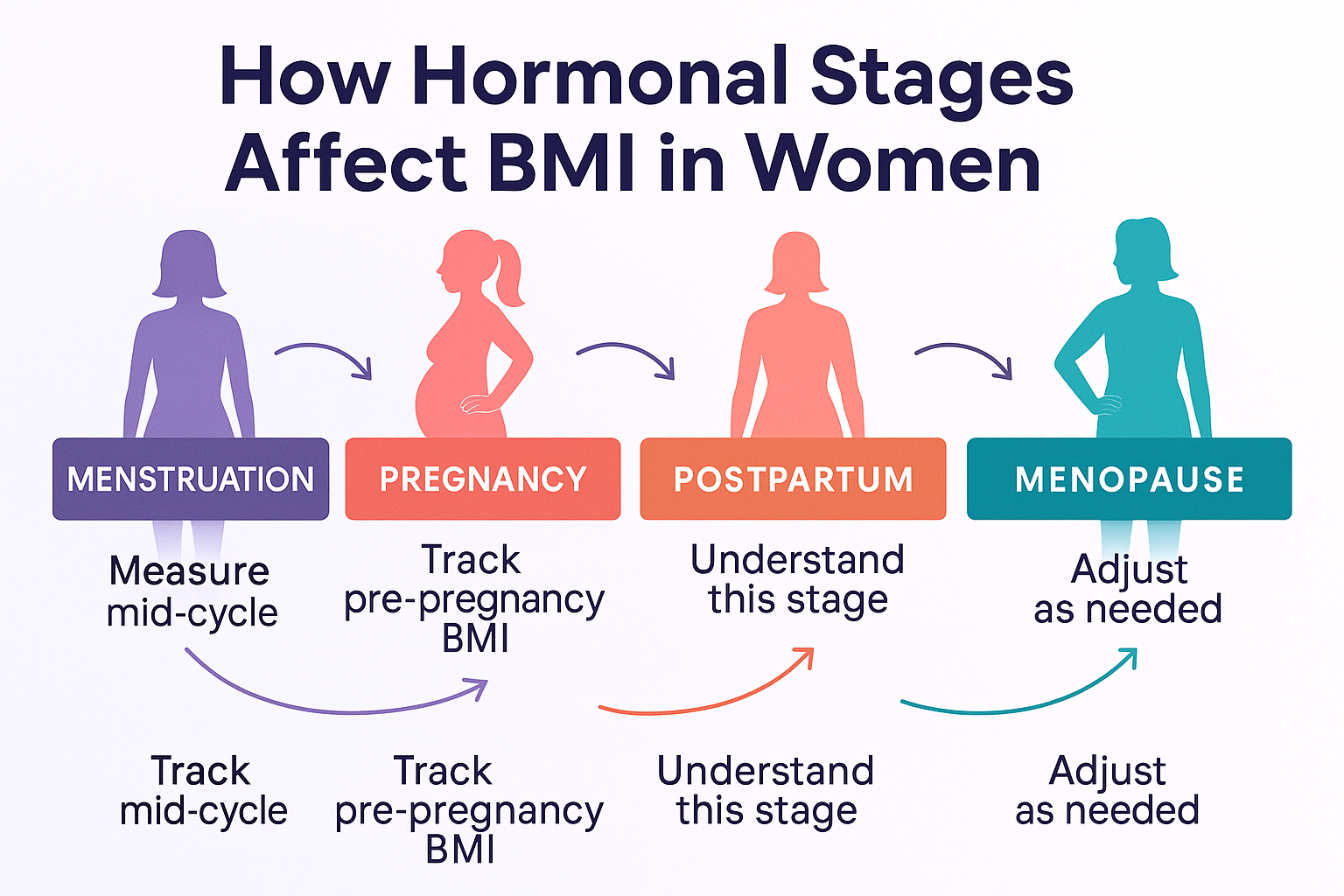
Hormonal Phases and BMI What to Know
How Your Hormones Influence Your BMI Over Time
Women’s bodies change significantly during different hormonal phases and so does how affect how female BMI range is calculated and understood. Unlike men, female weight and fat distribution are deeply tied to estrogen, progesterone, and other reproductive hormones that fluctuate throughout life.
Let’s break it down phase by phase.
Hormonal Phases That Impact Female BMI
1️⃣ Menstruation
- Bloating & water retention can temporarily raise weight
- BMI may vary slightly week to week
- Not an accurate time to measure for precise BMI comparison
- Tip: Weigh yourself mid-cycle for consistency
2️⃣ BMI and Pregnancy
- BMI is not used to assess weight during pregnancy
- Instead, doctors use pre-pregnancy BMI to set healthy weight gain targets
- Example:
- Normal pre-pregnancy BMI → gain 25–35 lbs
- Overweight pre-pregnancy BMI → gain 15–25 lbs
BMI and Pregnancy doesn’t goes together furing pregnancy, your pre-pregnancy weight determines your healthy BMI for women, helping guide expected weight gain.
Learn more in our Science and Data Behind BMI Calculations
3️⃣ Postpartum
- It’s normal for BMI to stay elevated for months after birth
- Hormonal recovery, sleep deprivation, and stress all affect metabolism
- Focus on long-term trends, not short-term changes
4️⃣ Menopause
- Drop in estrogen increases abdominal fat storage
- Women may gain weight even without changing habits
- BMI may rise even if lifestyle stays constant — waist circumference becomes more important
- Consider body composition tracking alongside BMI
During menopause, even without weight gain, your female BMI range might shift due to muscle loss and hormonal fat redistribution.
Also see: BMI and Lifestyle Guide for tips on managing body changes across life phases.
Compare BMI’s use cases in our BMI Accuracy, Risks & Misconceptions
See NIH guidelines for healthy BMI and pregnancy weight gain by BMI category.
“Your BMI doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause all shift your weight—and how that number should be read.”
Lifestyle, Muscle Mass & Female Body Composition
Why BMI Doesn’t Always Reflect the Full Picture for Women
One of the biggest limitations of BMI especially for women is that it doesn’t distinguish between fat and muscle. Women naturally carry more fat than men, but active, athletic women may have higher muscle mass that throws off their BMI classification.
Body Composition Basics for Women
- BMI ignores how weight is distributed, which can mislead health assessments
- Muscle is denser than fat → a muscular woman may appear “overweight” by BMI
- Essential body fat for women is higher than for men (about 10–13% vs 2–5%)
- Women store fat in hips, thighs, and breasts for reproductive health
Real-Life Example:
| Person | Height | Weight | BMI | Look/Reality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Office Worker | 5’5″ | 150 lbs | 25.0 | Slightly overweight |
| CrossFit Athlete | 5’5″ | 150 lbs | 25.0 | Lean, strong, low body fat |
Same BMI, very different health picture.
When BMI Fails and What to Use Instead
If you’re very active, or if you’re tracking changes due to menopause or postpartum recovery, consider combining BMI with these tools:
- Body fat percentage (via smart scale or calipers)
- Waist circumference
- Waist-to-hip ratio
- Strength or performance tracking
For better lifestyle-based strategies, explore the BMI and Lifestyle Guide
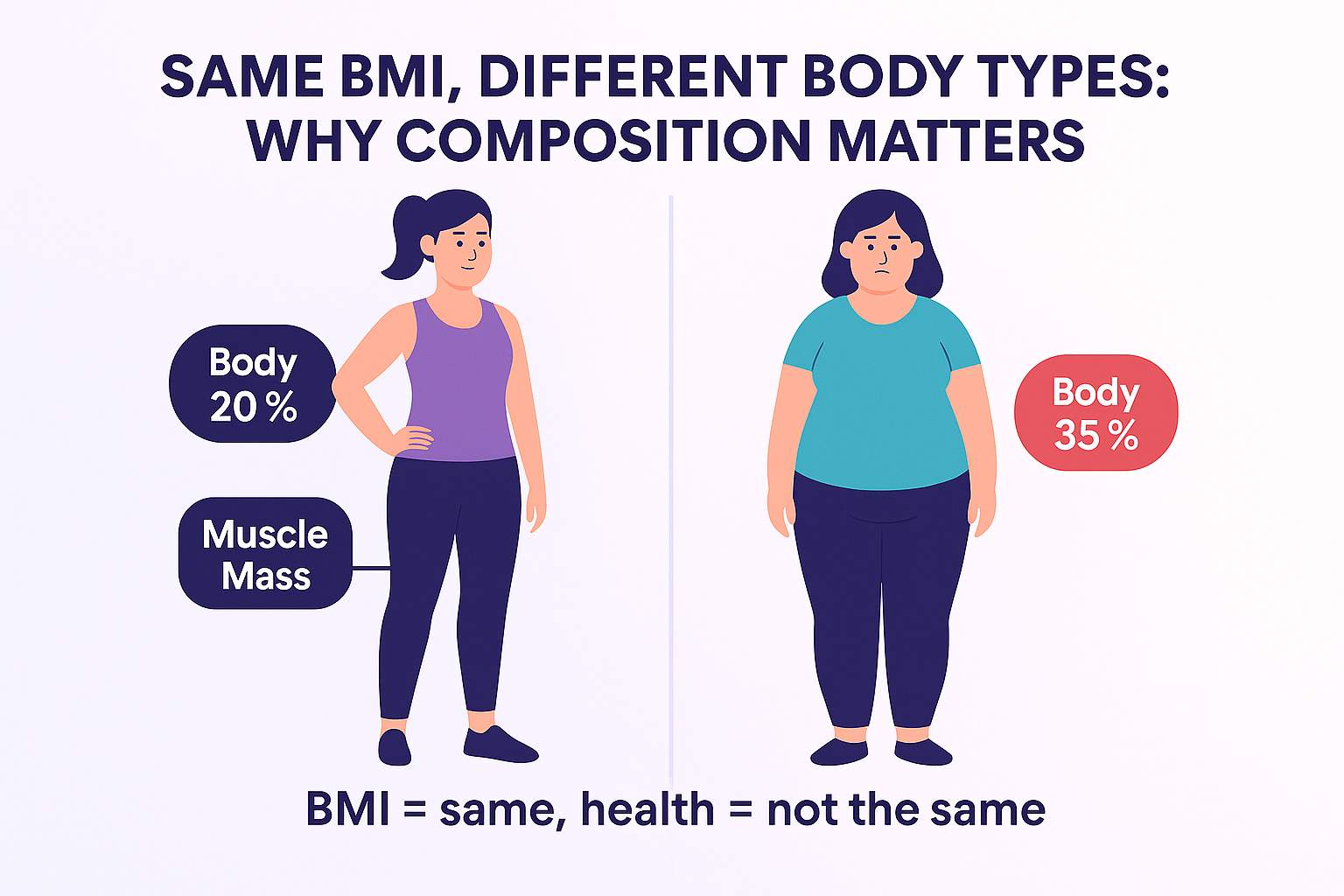
“Two women can have the same BMI and completely different health outcomes. BMI is a starting point—not the final word.”
How to Use It Right: BMI Guide for Women Step-by-Step
A Step-by-Step Guide to Get the Most Reliable Result
Using the BMI Calculator for Women is quick and easy — but accuracy depends on entering your height and weight correctly and understanding when and how to measure. Here’s how to do it right:
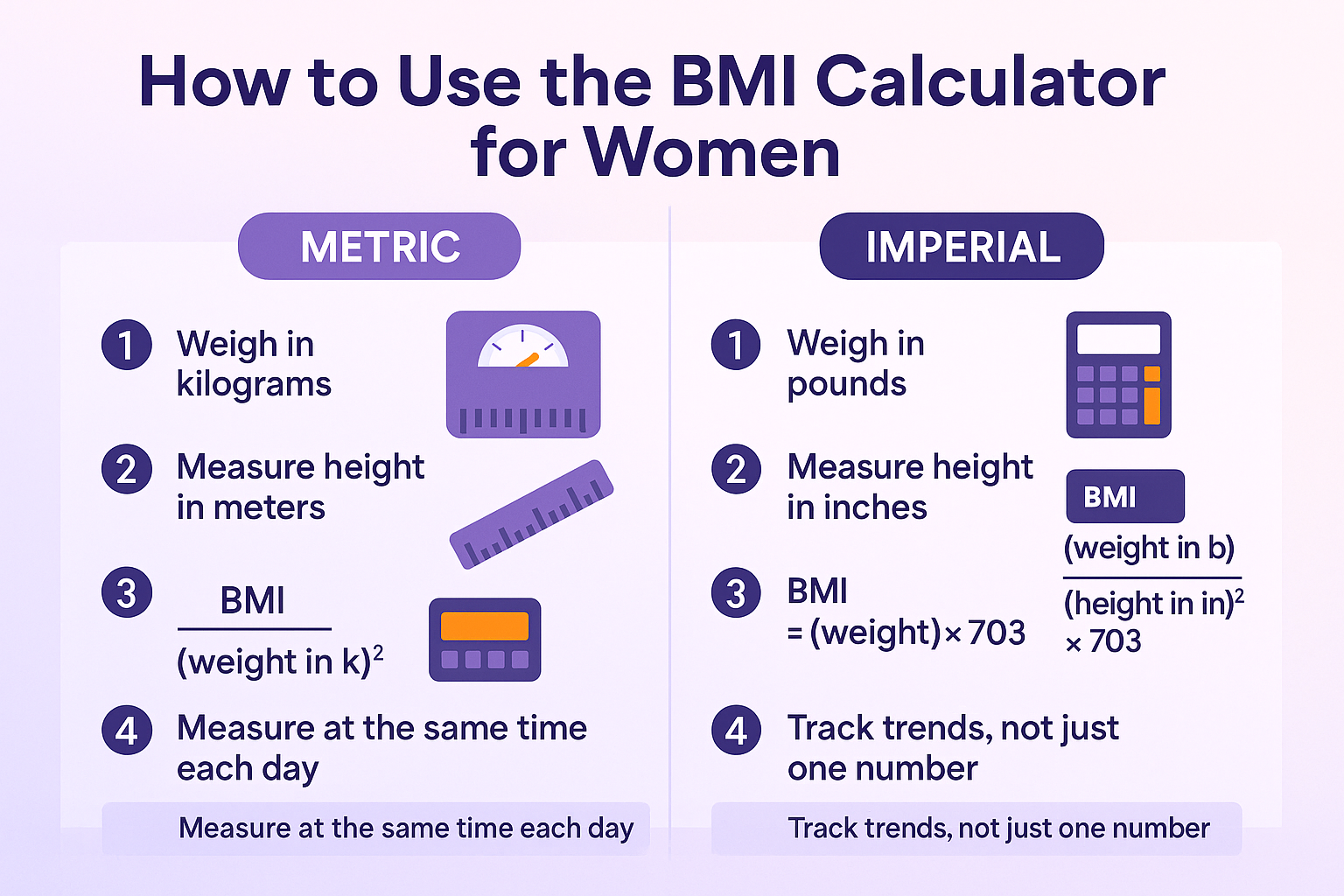
Step-by-Step: How to Calculate BMI (Women)
✅ Using Metric Units
- Step 1: Measure your weight in kilograms (kg)
- Step 2: Measure your height in meters (m)
- Step 3: Apply the formula:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²)
✅ Using Imperial Units
- Step 1: Measure your weight in pounds (lbs)
- Step 2: Measure your height in inches (in)
- Step 3: Apply the formula:
BMI = (weight (lbs) ÷ height² (in²)) × 703
Use your results to compare against the medically recommended healthy BMI for women, and check if further body composition analysis is needed. Try it instantly using the BMI Calculator for Women
Best Practices for Women:
- Measure height in the morning — your spine compresses slightly throughout the day
- Weigh yourself at the same time daily — ideally before eating
- Avoid checking BMI during menstruation — water retention can skew results
- For pregnant women, use pre-pregnancy BMI for accurate guidance
BMI Calc Tools You Can Try:
| Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| BMI Calculator for Women | General guidance for adult females |
| BMI Calculator for Teens | Age-specific, percentile-based tracking |
| BMI Calculator for Seniors | Adjusted for muscle mass loss |
| BMI Calculator for Kids | Pediatric percentile system |
| BMI Calculator for Men | For gender-specific muscle distribution |
| General BMI Calculator | All-purpose for any gender |
“The best BMI result starts with accurate input. Choose the right units, avoid hormonal fluctuation periods, and use your pre-pregnancy weight if expecting.”
When to Trust BMI: A Smart BMI Guide for Women
BMI Can Be Helpful If You Know Its Limits
The BMI Calculator for Women is a useful tool when used as a starting point not a diagnosis. It gives you a quick snapshot of where your weight may fall on a standard scale. But for women, that number often needs additional context.
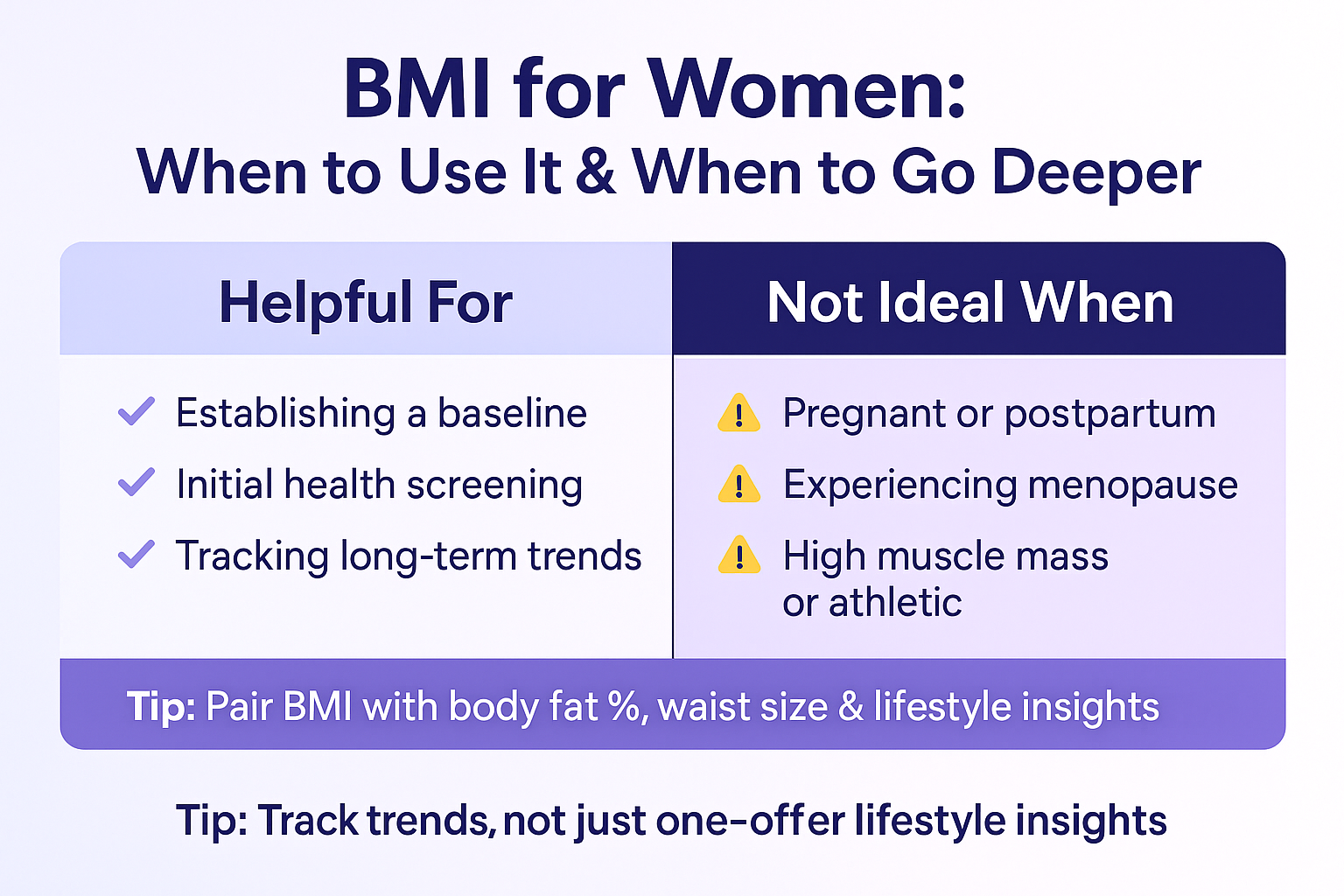
When BMI Is Helpful:
- To identify general weight category (underweight, normal, overweight)
- For setting a baseline before health or fitness plans
- For healthcare providers to screen for possible risks
- When tracking long-term weight trends
When BMI Can Be Misleading:
- During pregnancy or postpartum
- In very athletic women with high muscle mass
- During hormonal shifts (menstruation, menopause)
- If used alone, without considering lifestyle, body composition, or genetics
BMI doesn’t measure:
- Fat distribution
- Water retention
- Muscle mass
- Bone density
- Metabolic health
For a better understanding of BMI’s scientific strengths and limitations, visit our Science and Data Behind BMI.
What to Use Alongside BMI:
- Body fat %
- Waist circumference
- Waist-to-hip ratio
- Blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose levels
- Energy levels, sleep, and menstrual health
These combined give you a holistic picture of wellness, far beyond a number.
The Medline Plus offers insights into how aging impacts fat and muscle and how that affects BMI reliability.
“Think of BMI as a red flag, not a final verdict. It points to areas worth exploring—but it doesn’t know your hormones, lifestyle, or strength.”
Related BMI Calculators You Can Try
Find the Right BMI Tool for Every Life Stage and Body Type
Women’s health journeys are diverse from adolescence to motherhood, and through menopause and beyond. That’s why we offer a range of specialized BMI calculators to suit your current phase and goals.
Here are some tools you can explore to get the most accurate and personalized health insights:
Explore Our BMI Tools:
| Calculator | Best For |
|---|---|
| BMI Calculator for Women | Tailored for female hormonal & physiological factors |
| General BMI Calculator | Quick BMI check for any adult |
| BMI Calculator for Men | Accounts for higher muscle mass in men |
| BMI Calculator for Kids | Based on age-specific growth charts |
| BMI Calculator for Teens | For tracking BMI during puberty and development |
| BMI Calculator for Seniors | Adjusted for aging-related muscle and fat changes |
Pro Tip: Using the right calculator for your age and stage gives you more meaningful results. A 22-year-old athlete and a 55-year-old menopausal woman shouldn’t rely on the same BMI scale.
For a more informed approach to your health, use this BMI Guide for Women alongside tools like body fat %, waist size, and lifestyle assessments. Explore your results in context with our full breakdown of the healthy BMI for women by life stage.
“One size doesn’t fit all when it comes to BMI. Choose the calculator that reflects your stage of life and unique body to get the clearest picture.”
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a healthy BMI for women?
A healthy BMI for most adult women ranges from 18.5 to 24.9. However, factors like muscle mass, age, and hormone levels may affect how your BMI should be interpreted.
Can my menstrual cycle affect my BMI?
Yes. During menstruation, temporary water retention can increase your weight slightly, which may cause a mild fluctuation in BMI. It’s best to track BMI mid-cycle for consistency.
Is BMI accurate during pregnancy?
No. BMI is not a valid tool during pregnancy. Doctors use your pre-pregnancy BMI to determine a healthy weight gain range throughout pregnancy.
How does menopause affect my BMI?
Menopause causes hormonal shifts that may lead to fat being stored more around the abdomen. This can raise your BMI even if your weight hasn’t changed much.
Is a high BMI always bad for women?
Not always. Muscular or athletic women may have a higher BMI but low body fat. BMI should be evaluated with other metrics like body fat % and waist size.
How often should women check their BMI?
Checking BMI every 3 to 6 months is usually enough. Look for trends rather than daily changes, and consider tracking other indicators like body fat percentage over time.
What’s more important — BMI or body fat percentage?
Body fat percentage gives a clearer picture of your health, especially if you’re active. BMI is helpful for a quick estimate but can’t differentiate fat from muscle.
Does BMI work the same for older women?
Not exactly. As women age, muscle mass naturally declines, which can affect BMI accuracy. That’s why older adults may benefit more from body composition analysis than BMI alone.





